Fetch JWST TSO programs from STScI
This Python script shows how to fetch and parse the entire catalog of JWST TSO prgrams from the STScI website.
This tutorial is split into three sections:
1. Fetch TSO files
STScI provides the information for each JWST program in two files:
- the Astronomers Proposal Tool (APT) file (in .aptx format)
- the status file (in .xml format)
The APT files have to be then converted .xml format to be further parsed. This can be done using the STScI’s APT software. This will be done under the hood by Gen TSO, all we need to set is the path to the APT executable:
After you installed APT, search in your Application folders. The executable will be located inside the bin subfolder. We will need to get the absolute path to it, It should be something like:
/Applications/APT\\ 2025.1/bin/aptThe following script shows how to fetch the APT and status for the programs:
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
from gen_tso.utils import KNOWN_PROGRAMS
# KNOWN_PROGRAMS is a list containing all known TSO PIDs up to cycle 4
# Path to APT executable:
apt_command = '/Applications/APT\\ 2025.1/bin/apt'
# Fetch all TSO programs:
programs = KNOWN_PROGRAMS
cat.fetch_jwst_programs(programs, apt_command)After you installed APT on Linux, search for the folder where it was installed. The path to the executable should be something like this:
/home/user/ast/apt/APT_2025.1/APTThe following script shows how to fetch the APT and status for the programs:
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
from gen_tso.utils import KNOWN_PROGRAMS
# KNOWN_PROGRAMS is a list containing all known TSO PIDs up to cycle 4
# Path to APT executable:
apt_command = '/home/user/ast/apt/APT_2025.1/APT'
# Fetch all TSO programs:
programs = KNOWN_PROGRAMS
cat.fetch_jwst_programs(programs, apt_command)Either on a Linux or OSX machine, you can create an environmental variable in your bash pointing to the APT executable, e.g.:
export APT='/Applications/APT\ 2025.1/bin/apt'then you can directly use that environmental variable in the script. The following script shows how to fetch the APT and status for the programs:
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
from gen_tso.utils import KNOWN_PROGRAMS
# KNOWN_PROGRAMS is a list containing all known TSO PIDs up to cycle 4
# APT's environmental variable:
apt_command = 'APT'
# Fetch all TSO programs:
programs = KNOWN_PROGRAMS
cat.fetch_jwst_programs(programs, apt_command)To process one program takes a few seconds. Thus, to process the entire catalog will take some ~10 min.
Fetch specific programs
If you need the observations from a single program, you can use the programs argument with the desired PID(s):
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
# Fetch a single program
apt_command = 'APT'
programs = 3712
cat.fetch_jwst_programs(programs, apt_command)If you want observations from specific programs, you can use the programs argument with the desired PID(s):
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
# Fetch a set of programs
apt_command = 'APT'
programs = [2759, 3557, 3730, 4098]
cat.fetch_jwst_programs(programs, apt_command)By default, the cat.fetch_jwst_programs() function will store the files into a default folder inside the Gen TSO package, you can find that folder with this script:
>>> from gen_tso.utils import ROOT
>>> print(f'{ROOT}data/programs/')
/home/user/.../gen_tso/data/programs/To place them to a custom folder, use the output_folder argument.
2. Parse files to database
Once we have downloaded the .xml files of the JWST TSO programs, we can parse them to a human readable format and save their content to a csv file if desired. Here’s how:
from gen_tso import catalogs as cat
from gen_tso.utils import KNOWN_PROGRAMS
# KNOWN_PROGRAMS is a list containing all known TSO PIDs up to cycle 4
# A list of observations from all TSO programs
observations = cat.parse_program(KNOWN_PROGRAMS)Set the to_csv argument to save the observations to a .csv file.
from gen_tso import catalogs as cat
from gen_tso.utils import KNOWN_PROGRAMS
# KNOWN_PROGRAMS is a list containing all known TSO PIDs up to cycle 4
# Parse and save all programs to default .csv file
to_csv = 'jwst_tso_programs.csv'
observations = cat.parse_program(KNOWN_PROGRAMS, to_csv=to_csv)
# Thats all! Now we can take a look at the content:
observations[98]{'category': 'ERS',
'pid': '1366',
'pi': 'Batalha',
'cycle': 1,
'observation': '3',
'visit': '1',
'status': 'Executed',
'event': 'transit',
'target': 'WASP-39',
'target_in_program': 'WASP-39',
'ra': '14:29:18.3955',
'dec': '-03:26:40.20',
'instrument': 'NIRSPEC',
'mode': 'BOTS',
'disperser': 'G395H',
'filter': 'F290LP',
'subarray': 'SUB2048',
'readout': 'NRSRAPID',
'groups': 70,
'integrations': 465,
'duration': 10.56,
'date_start': datetime.datetime(2022, 7, 30, 20, 46, 32),
'date_end': datetime.datetime(2022, 7, 31, 6, 21, 30),
'plan_window': None,
'proprietary_period': 0,
'label': 'Transmission - WASP-39b : nirspec g395h',
'special_reqs': ['OrientRange', 'PeriodZeroPhase', 'TimeSeriesObservation'],
'phase_reqs': {'ZeroPhase': '2457792.356338',
'Period': '4.05527999 Days',
'PhaseStart': '0.95248',
'PhaseEnd': '0.96275'},
'period': 4.05527999,
'phase_start': 0.957615,
'phase_duration': 0.10850052304279982,
'planets': ['b']}Set the to_csv argument to a filename path to save the outputs programs to the specified file:
from gen_tso import catalogs as cat
# Save to a custom csv file:
pid = 3712
observations = cat.parse_program(pid, to_csv='jwst_program_3712.csv')
# That's all! now we can take a look at the content:
observations[0]{'category': 'GO',
'pid': '3712',
'pi': 'Cubillos',
'cycle': 2,
'observation': '1',
'visit': '1',
'status': 'Executed',
'event': 'transit',
'target': 'WASP-69',
'target_in_program': 'WASP-69',
'ra': '21:00:6.2319',
'dec': '-05:05:41.49',
'instrument': 'NIRSPEC',
'mode': 'BOTS',
'disperser': 'G395H',
'filter': 'F290LP',
'subarray': 'SUB2048',
'readout': 'NRSRAPID',
'groups': 5,
'integrations': 4115,
'duration': 8.27,
'date_start': datetime.datetime(2024, 9, 30, 6, 39, 59),
'date_end': datetime.datetime(2024, 9, 30, 14, 28, 11),
'plan_window': None,
'proprietary_period': 12,
'label': 'NIRSpec/G395H WASP-69b',
'special_reqs': ['PeriodZeroPhase', 'TimeSeriesObservation'],
'phase_reqs': {'ZeroPhase': '2455748.83422',
'Period': '3.8681382 Days',
'PhaseStart': '0.957128',
'PhaseEnd': '0.967900'},
'period': 3.8681382,
'phase_start': 0.962514,
'phase_duration': 0.0890824772841191,
'planets': ['b']}Default csv file
Note that there’s a special case that users might consider. gen_tso has a default csv file location that’s used to store/maintain all known programs.
Use the following script if you want to manually updated that file. Just be warned that if you do, make sure to store all known programs in there, otherwise gen_tso will be omitting programs that were not stored in there.
from gen_tso import catalogs as cat
from gen_tso.utils import KNOWN_PROGRAMS, ROOT
# Default csv file
to_csv = f'{ROOT}data/programs/jwst_tso_programs.csv'
observations = cat.parse_program(KNOWN_PROGRAMS, to_csv=to_csv)3. Playground
Now that we have a database of JWST TSO programs at hand, users can load them using the cat.load_programs() function.
Here are a few things you can do with this database.
List phase-curve progams
Here’s another example to show all phase-curve programs
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
# Without arguments, this will load all programs
observations = cat.load_programs()
# Use the catalog to cross check with NASA target names
catalog = cat.Catalog()
# List all phase curve programs
ntotal = 0
print(' N Program Obs Target Status')
print('--------------- -------------------------')
for obs in observations:
event = obs['event']
host = cat.get_observation_host(obs, catalog.targets)
# Host not yet in NASA Exoplanet Archive
if host is None:
host = obs['target']
if event == 'phase curve':
ntotal += 1
category = obs['category']
pid = obs['pid']
oid = obs['observation']
status = obs['status']
print(f"{ntotal:2} {category:>6} {pid} {oid:>3} {host:12s} {status}") N Program Obs Target Status
--------------- -------------------------
1 GTO 1201 1 WASP-121 Executed
2 GTO 1201 2 LTT 9779 Executed
3 GTO 1224 2 WASP-43 Executed
4 ERS 1366 11 WASP-43 Executed
5 GO 1729 1 WASP-121 Executed
6 GO 1803 1 GJ 1214 Executed
7 GO 2008 1 HD 80606 Executed
8 GO 2158 1 NGTS-10 Executed
9 GO 2159 1 K2-141 Executed
10 GO 2347 1 K2-141 Executed
11 GO 2488 1 HD 80606 Executed
12 GO 2508 1 GJ 367 Executed
13 SURVEY 2765 1 TOI-849 Withdrawn
14 SURVEY 2765 2 TOI-849 Withdrawn
15 SURVEY 2765 3 TOI-849 Withdrawn
16 SURVEY 2765 4 TOI-2109 Withdrawn
17 SURVEY 2765 5 TOI-2109 Withdrawn
18 SURVEY 2765 6 TOI-2109 Withdrawn
19 GO 3077 1 TRAPPIST-1 Executed
20 GO 3077 2 TRAPPIST-1 Executed
21 GO 3231 1 LTT 9779 Executed
22 GO 3263 1 TOI-1685 Executed
23 GO 3315 3 K2-22 Executed
24 GO 3784 1 TOI-2445 Executed
25 GO 3860 1 TOI-561 Executed
26 GO 4008 1 LHS 3844 Executed
27 GO 5022 1 WASP-103 Implementation
28 GO 5268 1 WASP-76 Executed
29 GO 7255 1 KELT-9 Implementation
30 GO 7255 2 KELT-9 Implementation
31 GO 8739 1 BD+05 4868 A Implementation
32 GO 8864 1 TOI-1807 Implementation
33 GO 8864 2 TOI-2260 Implementation
34 GO 8864 3 TOI-431 Implementation
35 GO 8864 4 TOI-2431 Implementation
36 GO 8864 5 TOI-6255 Implementation
37 GO 8877 1 TOI-2109 ImplementationAll programs for a target
Use the grouped=True argument to get a list of observations grouped per target (host)
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
# Observations grouper per host target
observations = cat.load_programs(grouped=True)
# Use the catalog to cross check with NASA target names
catalog = cat.Catalog()
targets = [
target for target in catalog.targets
if target.is_transiting
]
# List all programs targeting 'LHS 1140' (as named in NASA archive):
ntotal = 0
print(' N Program Obs Target Planets Event Status')
print('--------------- ----------------------------- ------')
for programs in observations:
host = cat.get_observation_host(programs[0], targets)
if host != 'LHS 1140':
continue
for obs in programs:
ntotal += 1
event = obs['event']
category = obs['category']
pid = obs['pid']
oid = obs['observation']
target = obs['target']
planets = obs['planets']
status = obs['status']
print(f"{ntotal:2} {category:>6} {pid} {oid:>3} {target:8s} {planets} {event:7} {status}") N Program Obs Target Planets Event Status
--------------- ----------------------------- ------
1 GO 2334 1 G 268-38 ['b'] transit Executed
2 GO 2334 2 G 268-38 ['b'] transit Executed
3 GO 3730 9 LHS 1140 ['c'] eclipse Executed
4 GO 3730 10 LHS 1140 ['c'] eclipse Executed
5 GO 3730 11 LHS 1140 ['c'] eclipse Executed
6 DD 6543 1 LHS 1140 ['b'] transit Executed
7 DD 6543 2 LHS 1140 ['b'] transit Executed
8 GO 7073 21 LHS 1140 ['b'] transit Implementation
9 GO 7073 22 LHS 1140 ['b'] transit Implementation
10 GO 7073 23 LHS 1140 ['b'] transit Implementation
11 GO 7073 24 LHS 1140 ['b'] transit Implementation
12 GO 7073 25 LHS 1140 ['b'] transit Implementation
13 GO 7073 26 LHS 1140 ['b'] transit Implementation
14 GO 7073 31 LHS 1140 ['c'] transit Implementation
15 GO 7073 32 LHS 1140 ['c'] transit Implementation
16 GO 7073 33 LHS 1140 ['c'] transit ImplementationGet targeted planet(s)
Now that we have the JWST programs information, we can cross-check with the NASA catalog of exoplanet to find out which planet(s) are targeted by each observation. This script find’s which planet belongs to each observation, and displays the info for multi-planet systems:
Note that the planet information is already contained in the cat.load_programs() output. This script is mostly a demo.
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
# Observations grouper per host target
observations = cat.load_programs()
# Will need to cross check with NASA catalog of transiting planets
catalog = cat.Catalog()
# Find the planet (by host name, labels, or phase constraints)
for obs in observations:
obs['planets'] = cat.get_planet_letters(obs, catalog.targets)
# Show planets in multi-planet systems
print('PID Obs Target Planets Event type')
print('-----------------------------------------------')
for obs in observations:
host = cat.get_observation_host(obs, catalog.targets)
pid = obs['pid']
oid = obs['observation']
target = obs['target']
all_planets = [
target.planet
for target in catalog.targets
if target.host == host
]
if len(all_planets) > 1:
event = obs['event']
planets = obs['planets']
print(f"{pid} {oid:>3} {host:12s} {repr(planets):10} {event}")PID Obs Target Planets Event type
-----------------------------------------------
1177 7 TRAPPIST-1 ['b'] eclipse
1177 8 TRAPPIST-1 ['b'] eclipse
1177 9 TRAPPIST-1 ['b'] eclipse
1177 10 TRAPPIST-1 ['b'] eclipse
1177 11 TRAPPIST-1 ['b'] eclipse
1185 8 WASP-107 ['b'] transit
1185 9 WASP-107 ['b'] transit
1201 8 WASP-107 ['b'] transit
1201 9 WASP-107 ['b'] eclipse
1201 502 WASP-107 ['b'] eclipse
...
6193 1 TOI-700 ['d'] transit
6193 2 TOI-700 ['e'] transit
6456 1 TRAPPIST-1 ['b', 'e'] transit
6456 2 TRAPPIST-1 ['b', 'e'] transit
6456 3 TRAPPIST-1 ['b', 'e'] transit
6456 4 TRAPPIST-1 ['b', 'e'] transit
6456 5 TRAPPIST-1 ['b', 'e'] transit
6456 15 TRAPPIST-1 ['b', 'e'] transit
6457 1 LP 791-18 ['d'] eclipse
6457 2 LP 791-18 ['d'] eclipse
6457 3 LP 791-18 ['d'] eclipse
6457 4 LP 791-18 ['d'] eclipse
6457 5 LP 791-18 ['d'] eclipse
6491 1 Kepler-167 ['e'] transit
...
8004 1 TOI-431 ['d'] transit
8004 2 TOI-431 ['d'] transit
8004 3 HIP 9618 ['b'] transit
8004 4 HIP 9618 ['b'] transit
8864 3 TOI-431 ['b'] phase curve
9025 3 WASP-84 ['b'] transitPlot spectral coverage
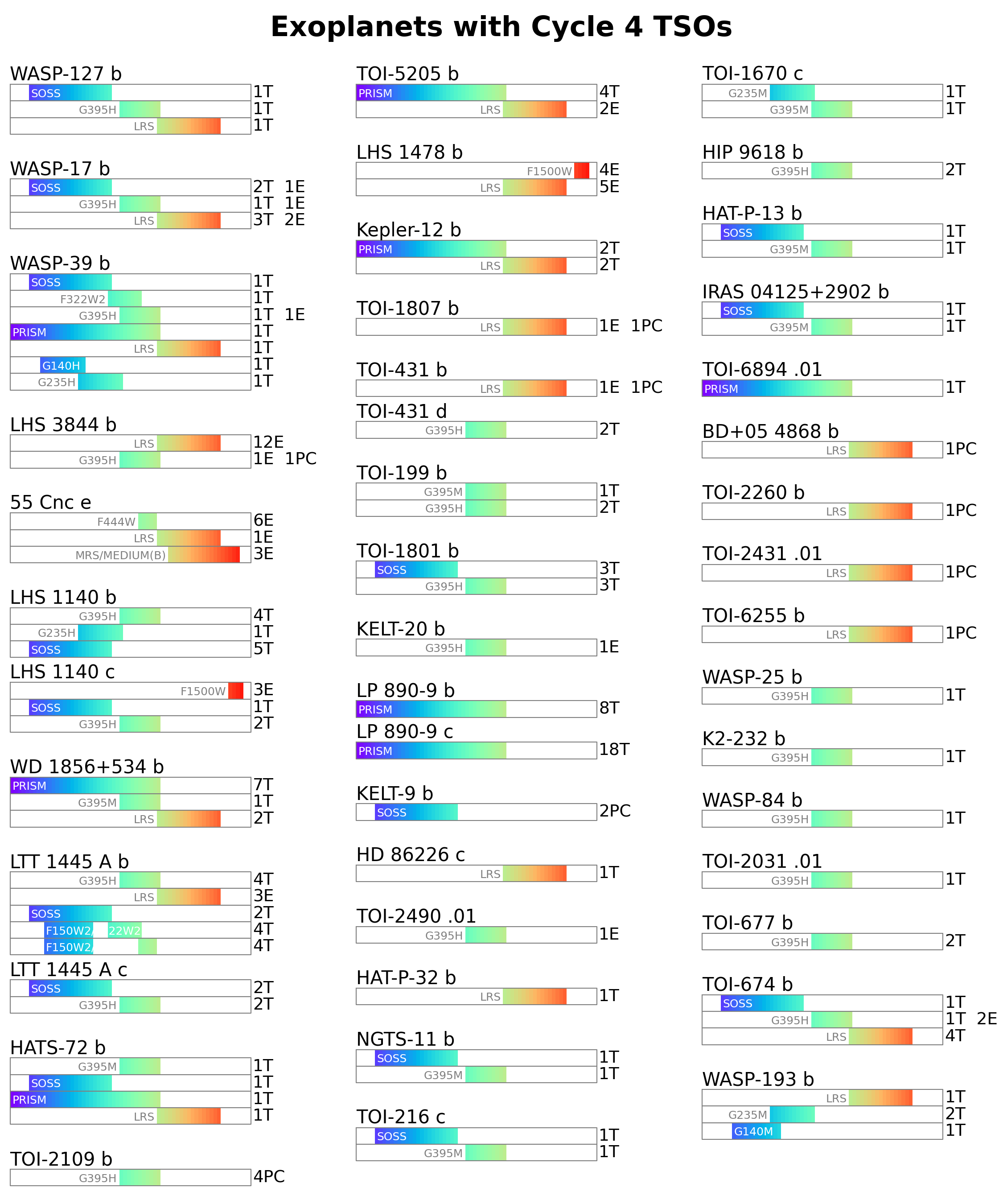
This script combines the various information from the programs to display the wavelength coverage for the systems targeted in cycle 4.
import gen_tso.catalogs as cat
import gen_tso.pandeia_io as jwst
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.image import BboxImage
from matplotlib.transforms import Bbox, TransformedBbox
plt.ion()
# First define a few convenient functions to handle the data
def get_band_width(inst, mode, disperser, filter, subarray):
"""Get the wavelength edges for the observing configuration"""
wl_min2, wl_max2 = 0, 0
if mode == 'lrs':
mode = 'lrsslitless'
filter = 'None'
elif mode == 'mrs':
mode = 'mrs_ts'
filter = disperser[0:disperser.index('(')]
elif mode == 'imaging ts':
mode = 'imaging_ts'
subarray = 'imager'
elif mode == 'grismr ts':
mode = 'lw_tsgrism'
filters = filter.split(',')
filter = filters[1]
if 'dhs0' in disperser:
mode2 = 'sw_tsgrism'
filter2 = filters[0]
wl_min2, wl_max2 = jwst.get_bandwidths(
inst, mode2, subarray, filter2,
)[2:4]
elif mode == 'soss':
filter = 'clear'
subarray = subarray.replace('full', 'sossfull')
elif mode == 'bots':
filter = f'{disperser}/{filter}'
wl_min, wl_max = jwst.get_bandwidths(inst, mode, subarray, filter)[2:4]
if wl_min2 != 0:
return [wl_min, wl_min2], [wl_max, wl_max2]
return [wl_min], [wl_max]
def make_passband(wl_min, wl_max):
"""Make a colormap array coloring specified wl ranges"""
ncol = 64
band = np.zeros((2,ncol,4))
wl = np.logspace(np.log10(0.65), np.log10(18), ncol)
for i in range(ncol):
band[:,i] = plt.cm.rainbow(i/(ncol-1))
passband = np.zeros(ncol, bool)
for wmin, wmax in zip(wl_min, wl_max):
passband |= (wl >= wmin) & (wl<=wmax)
band[:,:,3] = passband
return band
def collect_configs(programs):
"""
Split observations by mode and event, count them, and
collect wavelenght coverage.
"""
configs = {}
for j,obs in enumerate(programs):
inst = obs['instrument'].lower()
mode = obs['mode'].lower()
disperser = obs['disperser'].lower()
filter = obs['filter'].lower()
subarray = obs['subarray'].lower()
if mode == 'lrs':
label = 'LRS'
elif mode == 'mrs':
label = f"MRS/{obs['disperser']}"
elif mode == 'imaging ts':
label = obs['filter']
elif mode == 'soss':
label = 'SOSS'
elif mode == 'bots':
label = obs['disperser']
elif mode == 'grismr ts':
filters = obs['filter'].split(',')
if 'dhs0' in disperser:
label = '/'.join(filters)
else:
label = filters[1]
event = obs['event'][0].upper()
if label not in configs:
configs[label] = {'T': 0, 'E': 0, 'P': 0}
configs[label][event] += 1
wl_min, wl_max = get_band_width(inst, mode, disperser, filter, subarray)
configs[label]['wl_min'] = wl_min
configs[label]['wl_max'] = wl_max
return configs
def make_label(config):
label = ''
if config['T'] > 0:
label += f"{config['T']}T "
if config['E'] > 0:
label += f"{config['E']}E "
if config['P'] > 0:
label += f"{config['P']}PC"
return label.strip()
# Now lets plot
# JWST observations grouped by host:
observations = cat.load_programs(grouped=True)
# For target cross-checking only with transiting planets
targets = [
target for target in cat.Catalog().targets
if target.is_transiting
]
# Plot planets targeted in Cycle 4
fs = 10
dx = 0.24
h = 0.0138
dtx = 0.002
x0 = 0.01
y0 = 0.93
fig = plt.figure(0)
plt.clf()
fig.set_size_inches(7.5,9)
plt.subplots_adjust(0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0)
ax = plt.subplot(111)
plt.axis('off')
ax.set_xlim(0, 1)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1)
title = 'Exoplanets with Cycle 4 TSOs'
ax.text(0.5, 0.97, title, fontsize=15, weight='bold', ha='center')
for programs in observations:
cycles = [obs['cycle'] for obs in programs]
if 4 not in cycles:
continue
if y0 < 0.02:
x0 += 0.345
y0 = 0.93
host = cat.get_observation_host(programs[0], targets)
if host is None:
host = programs[0]['target']
all_planets = np.concatenate([obs['planets'] for obs in programs])
for planet in np.unique(all_planets):
planet_name = f'{host} {planet}'
ax.text(x0, y0, planet_name, fontsize=fs, ha='left', va='bottom')
progs = [obs for obs in programs if planet in obs['planets']]
configs = collect_configs(progs)
for label,config in configs.items():
x1 = x0 + dx
y1 = y0 - h
band = make_passband(config['wl_min'], config['wl_max'])
ax.plot(
[x0, x1, x1, x0, x0], [y0, y0, y1, y1, y0],
lw=0.5, c='0.5',
)
bbox = TransformedBbox(Bbox.from_bounds(x0,y1,dx,h), ax.transAxes)
ax.add_artist(BboxImage(bbox, cmap='rainbow', data=band))
obs_label = make_label(config)
ax.text(x1+dtx, y1, obs_label, fontsize=fs-1, ha='left', va='bottom')
b0 = np.where(band[0,:,3])[0][0]/64
xt = x0 + dx*b0 + dtx * (-1)**int(b0 >= 0.2)
yt = y0-0.9*h
ha = 'left' if b0 < 0.2 else 'right'
col = 'w' if b0 < 0.2 else '0.5'
ax.text(xt, yt, label, color=col, fontsize=fs-4, ha=ha, va='bottom')
y0 -= h
y0 -= 1.5*h
y0 -= 1.2*h
plt.savefig('family_portrait_cycle4.png', dpi=300)